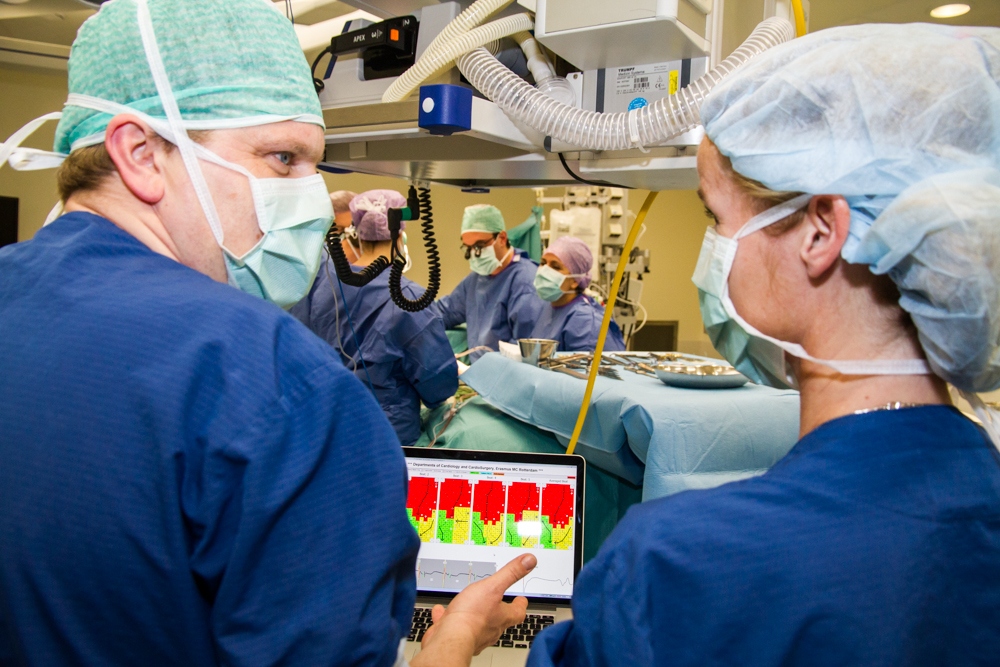
What is atrial fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation is the cardiac arrhythmia of the 21st century
Currently, atrial fibrillation (also called AF) is one of the most common cardiac arrhythmias. Although it is not life-threatening, it must be treated in order to prevent further damage. So, what exactly is heart disease and what are the symptoms?
What is known about AF so far:
- Atrial fibrillation causes electrical disturbances in the atria
- Atrial fibrillation often causes a high and irregular heartbeat
- According to patients, atrial fibrillation reduces their quality of life
- This heart disease occurs in both older and younger people
- Atrial fibrillation increases the risk of stroke and heart failure
- The origin of atrial fibrillation is still unclear
- Current treatments work only in 50% of patients
What happens during atrial fibrillation?
In order to understand atrial fibrillation, you first need more background information surrounding the heart. This is, after all, the largest, most important muscle in our bodies.
The heart muscle has 4 cavities and pumps blood throughout the body. The upper two cavities are called the atria, the lower two cavities are called the ventricles. They are separated by the heart valves.
During atrial fibrillation, electrical currents in the atrial disrupt the atrial rhythm. As a result, the atria and ventricle do not contract evenly, resulting in a rapid, irregular heartbeat. Oxygen deficiency occurs in the heart muscle, causing the patient to experience chest pain.
Is atrial fibrillation dangerous?
AF is not directly and strictly life-threatening, but it does increase the risk of other conditions. For example, people with atrial fibrillation are five to seven times more likely to have blood clots or a stroke. The cardiac arrhythmia can also cause heart failure and damage to the atrial heart cells.
Atrial fibrillation increases the risk of:
- A stroke
- Heart failure
- Damage to the atrial heart cells
What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation?
Common symptoms of AF are:
- Palpitations
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
Unfortunately it’s challenging to directly associate symptoms with AF. We always recommend you to see your doctor in case you suspect having AF.
Wat is de oorzaak van boezemfibrilleren?
There is no single clear cause of atrial fibrillation. However, there are several risk factors that are known to increase the risk of heart disease.
Risk factors:
- Aging
- An unhealthy lifestyle
- High blood pressure
- Heart valve abnormality
- Disturbed thyroid function
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Atrial fibrillation occurs more often in men than in women
How is atrial fibrillation diagnosed?
Atrial fibrillation can occur in two different ways. The arrhythmia can be present in attacks (paroxysmal) or on the other hand, it may take place continuously (persistent/permanent).
If you think you may be suffering from atrial fibrillation, it can be swiftly determined with an electrocardiogram or a Holter. There are however few cases in which these methods are not effective, and other means of diagnosis are needed.
How is atrial fibrillation treated?
Taking into account the severity of the repercussions of atrial fibrillation, treatment is paramount.
Currently, there are three treatments available: drugs, ablation and cardioversion. Moreover, you can reduce risk factors by implementing changes in your lifestyle.
GGA and L-Glutamine as potential new AF treatments
Unfortunately, atrial fibrillation relapses happen far too often. This is why we are making an effort to investigate new, promising treatments such as GGA and L-Glutamine.
Share this article